| Page 1 out of 25 Pages |
Refer to the exhibit.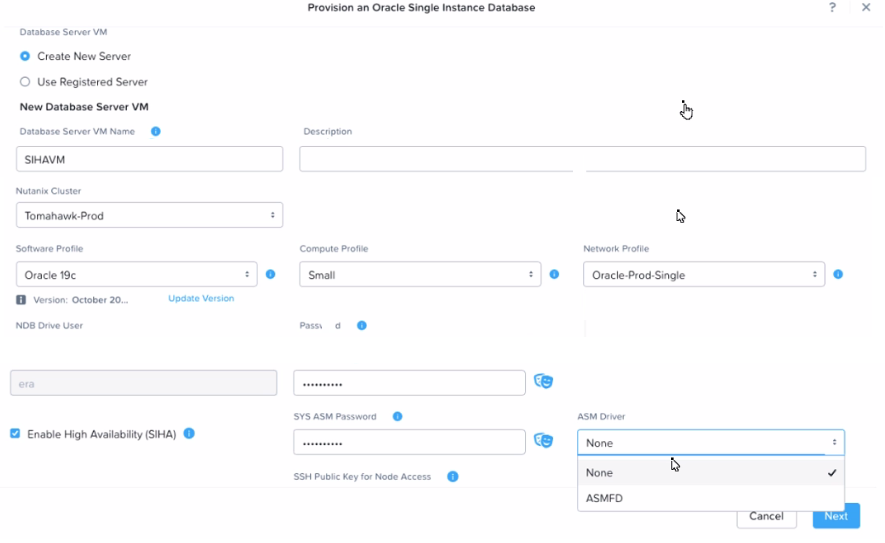
A request is received to provision a new Oracle SIHA DB & VM to test ASMLIB on OEL79 and Oracle 19c.
When walking through the provisioning workflow, only ASMFD is available in the ASM Driver drop down.
What is necessary to provision the requested SIHA DB and DB VM with ASMLIB?
A. Update the software profile to include the ASMLIB driver.
B. Install ASMLIB on the NDB server.
C. Update the NDB driver config to enable ASMLIB for Oracle.
D. Install ASMLIB on the database server
Explanation:
In the context of Nutanix Database Automation (NCP-DB), when provisioning a new Oracle SIHA DB &
VM, if only ASMFD is available in the ASM Driver drop-down, it indicates that ASMLIB is not included in
the current software profile. To provision the requested SIHA DB and DB VM with ASMLIB, it’s essential to
update the software profile to include the ASMLIB driver. This action will enable ASMLIB as an option in
the ASM Driver drop-down during the provisioning workflow.
Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator is receiving critical NDB email alerts regarding storage for the DBA database, which is a
member of a database group.
How would the administrator remediate the issue within NDB?
A. From the Database Summary page for the DBA database, use the Scale option to grow the storage accordingly.
B. From the Databases page, select the Database group and Scale the storage from the Database Actions menu.
C. From Prism Central, add additional storage to the VM, then expand the log storage via the database tools.
D. From the Alerts page, select the alert, choose Set Status to Resolved, and Scale the storage via the Resolve Now dialogue box.
Explanation: The administrator can remediate the issue of critical storage alerts by scaling up the storage directly from the Database Summary page for that specific DBA database. This action allows for an increase in storage capacity to alleviate space constraints and prevent future critical alerts related to storage space1. The other options are not correct, as they either involve scaling the entire database group, which may not be necessary or desired, or require additional steps outside of NDB, which may not be feasible or efficient.
Refer to the exhibit.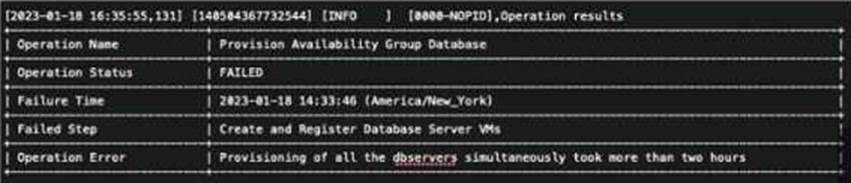
An administrator attempts to provision their first clustered database environment with NDB. The operation
fails with the Operation Error shown in the exhibit.
Which database engine was being deployed during this operation?
A. Oracle
B. MySQL
C. Microsoft SQL
D. PostgreSQL
Explanation:
The error message in the exhibit indicates that the operation failed during the “Create and Register Database
Server VMs” step because “Provisioning of all the observers simultaneously took more than two hours.” This
type of error is associated with MySQL, as it involves observers which are a part of MySQL Group
Replication, used for ensuring high availability1. The other options are not related to the error message, as
they do not use observers or Group Replication for clustering.
Refer to the exhibit.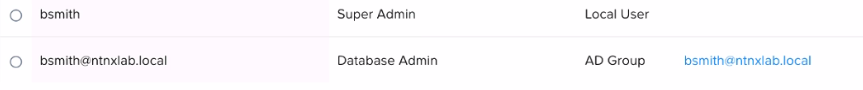
An administrator, whose accounts are shown in the exhibit, is trying to add a new database admin as a local
user to NDB, but is unable to complete the task.
What is most likely the cause of the issue?
A. The administrator is logged in with the Super Admin account.
B. An email address is required for the Super Admin account.
C. The administrator is logged in with the Database Admin account.
D. Only users in the domain admins group can create local users.
Explanation:
Based on the exhibit, the administrator is logged in with the Database Admin account (bsmith@ntnxlab.local),
which does not have the permission to create local users on NDB. Only the Super Admin account (bsmith)
has this permission, as indicated by the User type column. Therefore, the administrator needs to log out and
log in again with the Super Admin account to add a new database admin as a local user to
NDB.
Which ports must be open between the NDB server and Controller VMs to facilitate iSCSI connections?
A. 22 and 9440
B. 80 and 443
C. 3205 and 3260
D. 5985 and 5986
Explanation:
According to the Nutanix Database Automation (NCP-DB) course, the ports 3205 and 3260 are required for
iSCSI connections between the NDB server and the Controller VMs1. Port 3205 is used for the NDB iSCSI
initiator service, which initiates the iSCSI sessions and sends SCSI commands to the Controller VMs1. Port
3260 is used for the iSCSI target service, which listens for incoming iSCSI requests and provides access to the
storage devices on the Controller VMs1. The other options are not related to iSCSI connections. Port 22 is
used for SSH, port 9440 is used for Prism Central, port 80 is used for HTTP, port 443 is used for HTTPS, port
5985 is used for WinRM HTTP, and port 5986 is used for WinRM HTTPS2.
An administrator needs to add a stretched VLAN across two clusters in NDB. Which two prerequisites should be met prior to completing this action? (Choose two.)
A. VLAN must be IPAM.
B. VLAN must be static.
C. Both clusters must be registered in NDB.
D. Nutanix Cluster Management must be enabled.
Explanation:
A stretched VLAN is a virtual network that spans across multiple Nutanix clusters and allows the
communication between VMs on different clusters using the same subnet. A stretched VLAN can be used to
provide high availability and load balancing for NDB components, such as HAProxy VMs, that require a
virtual IP address (VIP) to be accessible from any cluster. To add a stretched VLAN across two clusters in
NDB, the administrator needs to meet two prerequisites: the VLAN must be static and both clusters must be
registered in NDB. A static VLAN is a VLAN that is manually created and configured by the administrator,
as opposed to an IPAM VLAN that is automatically created and managed by NDB. A static VLAN can be
added to a stretched VLAN in NDB, while an IPAM VLAN cannot. Both clusters must be registered in NDB
before adding a stretched VLAN, as NDB needs to have the information and access to the clusters and their
networks. The administrator can register the clusters in NDB using the Prism Element details, agent network
configuration, and storage container information. The other option, Nutanix Cluster Management, is not a
prerequisite for adding a stretched VLAN in NDB. Nutanix Cluster Management is a feature that allows the
administrator to manage multiple Nutanix clusters from a single NDB UI, such as creating or deleting
clusters, adding or removing nodes, or performing cluster operations. Nutanix Cluster Management is not
required for adding a stretched VLAN, as the VLANs are created and configured in Prism Element, not in
NDB.
| Page 1 out of 25 Pages |