| Page 3 out of 30 Pages |
Refer to the Exhibit: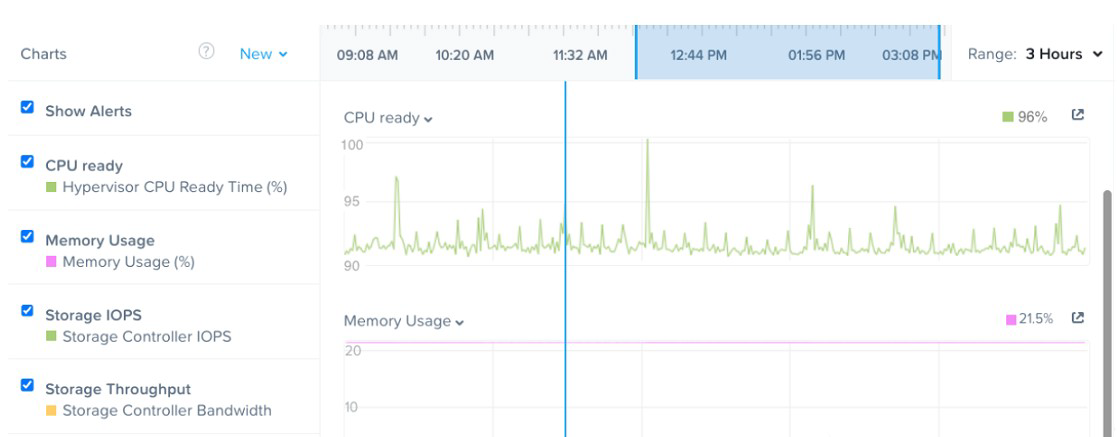
An administrator receives complaints of poor performance in a particular VM.
Based on the VM performance metric, what is the most likely cause of this behavior?
A. Oplog is full cannot serve IO request from this VM.
B. The host’s CPU is severely overloaded.
C. SSD tier is not big enough to serve workloads’ IOPS demand.
D. The VM needs more vCPUs
Explanation: Based on the VM performance metrics shown in the exhibit, the most likely
cause of the poor performance in the particular VM is that the host’s CPU is severely
overloaded. This is indicated by the high percentage of Hypervisor CPU Ready Time,
which is shown as 96% in the CPU ready chart. CPU Ready Time is a metric that shows
the amount of time a VM is ready to run but is unable to run because the host CPU
resources are not available. In a healthy environment, this value is typically low. A high
percentage indicates that the VMs are waiting for available CPU cycles, which means the
CPU is not able to schedule the VM effectively, often due to over commitment or heavy
CPU load.
When the CPU ready time is consistently high, it is a clear indicator that the VM is
frequently waiting for CPU resources, which can lead to performance issues such as
sluggishness or delays in processing. It is not related to the storage subsystem (Oplog
fullness or SSD tier size), nor directly to the number of vCPUs assigned to the VM. While
adding more vCPUs might seem like a solution, it could actually exacerbate the issue if the
host is already CPU constrained.
To resolve this issue, an administrator should consider balancing the load across the hosts
more effectively, possibly by using Nutanix's built-in automation and balancing features, or
by scaling out the cluster to add more CPU resources. It is also advisable to check for any
VMs with unusually high CPU demand and to adjust resource allocation as needed.
Nutanix provides extensive documentation and guidelines in their Resource Management
Guide to help administrators identify and resolve such performance issues.
Refer to the exhibit.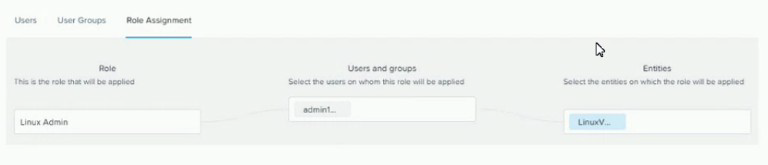
The Linux Admin role has been created to manage only Linux VMs in the environment.
However, the Admin1 user does not have access to all Linux VMs.
What step should be taken to grant the proper access?
A. Add the hosts to the entities KM for the role.
B. Grant the admin1 user the viewer role (or the cluster.
C. Add the role to the Linux images.
D. Add the proper category to each Linux VM.
Explanation: According to the Nutanix Prism Central Guide, role-based access control
(RBAC) in Prism Central allows you to create custom roles and assign them to users or
groups based on the categories of the entities they need to manage1. Categories are keyvalue
pairs that you can assign to entities such as VMs, hosts, clusters, images, etc. to
group them logically2. For example, you can create a category key called “OS” and assign
values such as “Linux” or “Windows” to different VMs based on their operating system.
In the exhibit, the Linux Admin role has been created with the following settings:
The role has the “VM Admin” permission, which allows the user to perform all
actions on VMs3.
The role has been assigned to the admin1 user.
The role has been scoped to the entities that have the category key “OS” and the value “Linux”.
However, the admin1 user does not have access to all Linux VMs in the environment. This
means that some of the Linux VMs do not have the proper category assigned to them. To
grant the proper access, the administrator should add the category key “OS” and the value
“Linux” to each Linux VM that needs to be managed by the Linux Admin role. This can be
done either individually or in bulk through Prism Central4. Once the categories are added,
the admin1 user will be able to see and manage all Linux VMs in the environment.
Which component can be associated with a storage policy?
A. Subnet
B. Catalog
C. Vm
D. Category
Explanation: A storage policy can be associated with a VM. A storage policy is a set of rules that define how data objects are stored and protected. It specifies the characteristics of storage, data protection, and data placement for virtual disks that are assigned to a VM. Subnets, catalogs, and categories are not associated with storage policies.
Refer to exhibit: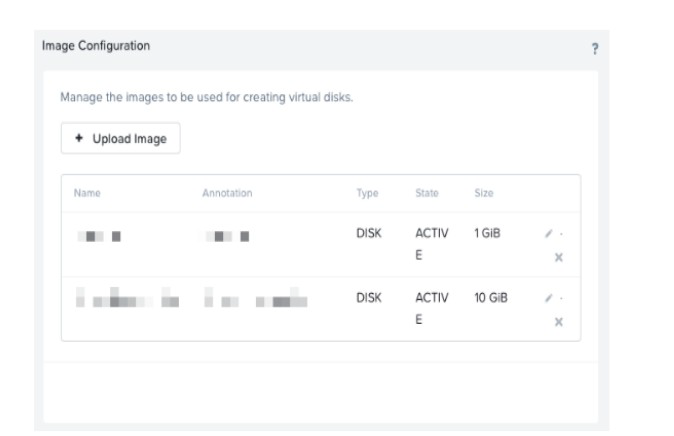
An
administrator needs to update some images that were previously uploaded to their Nutanix
cluster, while logged into Prism Element when trying to update the images, the update icon
is not enabled.
What could be the cause for this behavior?
A. RBAC is configured and the administrator's user doesn't have the right privileges.
B. The files were ISO but were uploaded as disk images hence cannot be used or edited.
C. Images are corrupted and must be re-uploaded.
D. Images were imported into Prism Central.
Administrator is creating a Windows 10 VM that will be used for a virtual desktop template.
After creating the VM and booting to the ISO, the administrator is unable to install Windows
and receives the following error.
What steps does the administrator need to take to install the OS?
A. Load the Nutanix VirtIO Serial Bus Driver.
B. Load the VirtIO Network Ethernet Adaper.
C. Load the Nutanix Virtual Balloon Driver.
D. Load the Virtual SCSI pass-through controller.
Explanation: Answer: D. Load the Virtual SCSI pass-through controller.
The error message shown in the image indicates that Windows 10 setup cannot find any
drives to install the OS. This is because the Nutanix AHV hypervisor uses a virtual SCSI
pass-through controller to present disks to the VMs, and Windows 10 does not have a builtin
driver for this device. Therefore, the administrator needs to load the Nutanix VirtIO driver
for the virtual SCSI pass-through controller during the OS installation process. The Nutanix
VirtIO driver package contains various drivers that are specifically used by Windows VMs
hosted in the Nutanix environment to enhance their stability and performance1. The
administrator can download the latest Nutanix VirtIO driver package from the VirtIO
downloads page of the Nutanix support portal. The administrator can then follow these
steps to load the driver and install the OS2:
On the Windows 10 setup screen, click Load driver.
Insert a USB drive or mount an ISO image that contains the Nutanix VirtIO driver
package.
Browse to the location of the driver package and select the folder that matches the
OS architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
Select the vioscsi.inf file and click Next.
Wait for the driver to load and then click Refresh.
Select the disk where you want to install Windows 10 and click Next.
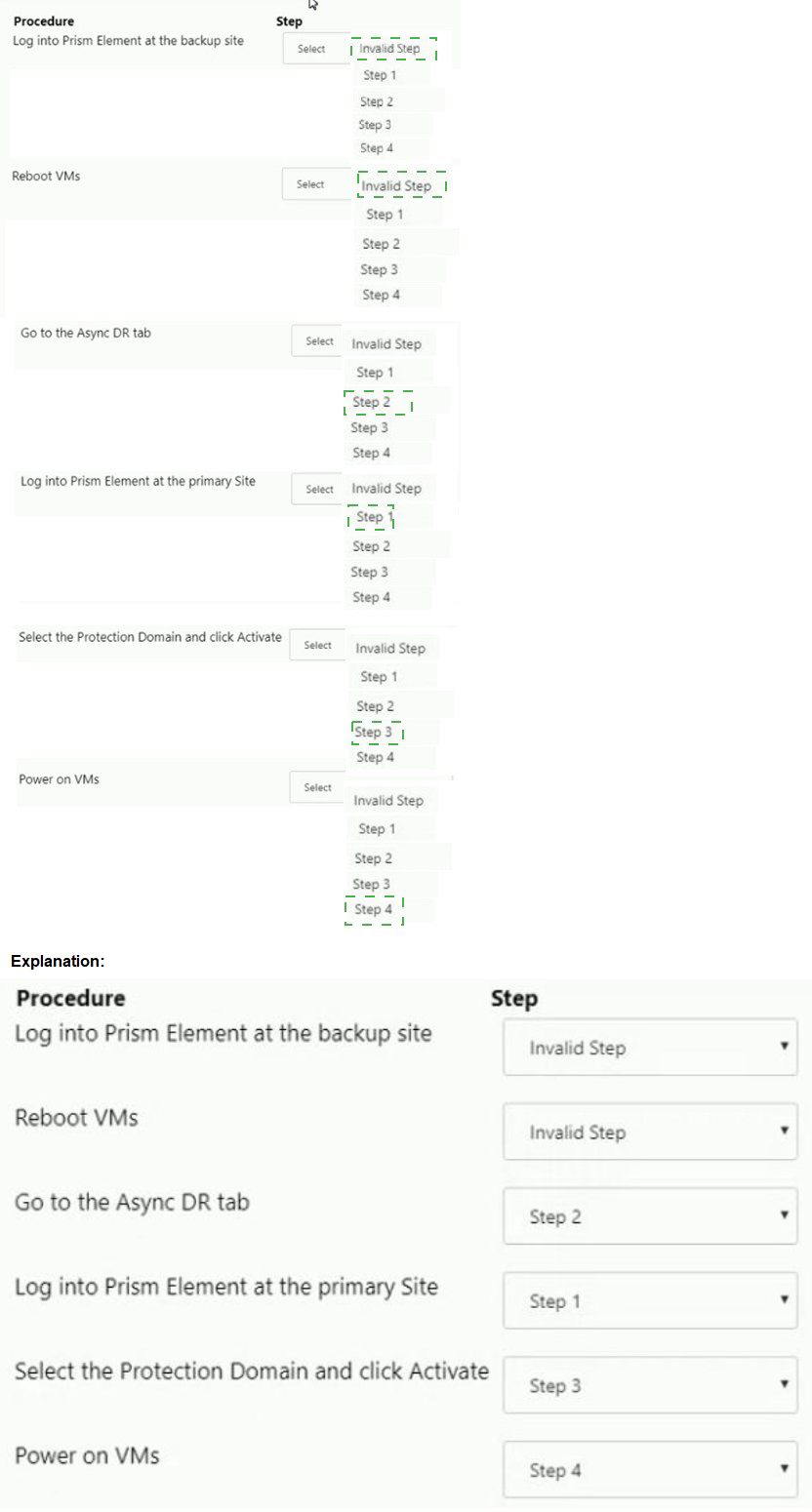
Async DR is configured between two sites. A network outage occurs at the primary site.
Which steps must the administrator perform to bring the VMs back into service at the
backup site?
Item instructions: For each procedure, indicate the order in which that procedure must take
place to meet the item requirements. Not all procedures are valid. Identify any invalid
procedures using the drop-down option.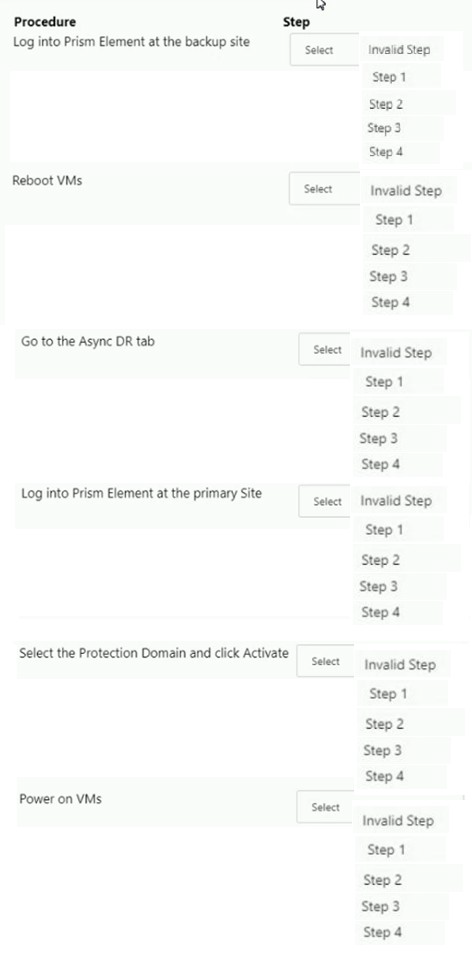
| Page 3 out of 30 Pages |
| Previous |