| Page 5 out of 30 Pages ... Showing Questions in Random order from Exam |
An administrator is tasked with configuring networking on an AHV cluster and needs to optimize for maximum single VM throughput.
Which bond mode should the administrator select?
A. Active-Active with Mac pinning
B. Active-Active
C. Active-Backup
D. No Uplink Bond
Explanation:
Active-Active is a bond mode that allows all uplinks in the bond to be used simultaneously for traffic transmission and reception. This bond mode provides load balancing and increased bandwidth for the AHV host and its VMs. Active-Active bond mode uses a hashing algorithm based on source MAC addresses to distribute traffic across different uplinks in the bond. Each individual VM NIC uses only a single bond member interface at a time, but multiple VM NICs are spread across different bond member interfaces. As a result, it is possible for a Nutanix AHV node with two 10 Gb interfaces to use up to 20 Gbps of network throughput, while individual VMs have a maximum throughput of 10 Gbps6.
Therefore, if an administrator needs to optimize for maximum single VM throughput, they should select Active-Active bond mode for their AHV cluster. This bond mode can be configured using Prism Element UI or manage-ovs commands on each AHV host7. No additional configuration is required on the upstream switch side, as long as the switches are interconnected physically or virtually and both uplinks trunk the same VLANs8.
Prism Central will be installed manually on an AHV cluster.
Which three disk images must be downloaded from the portal for the Prism Central VM? (Choose three.)
A. var
B. tmp
C. boot
D. home
E. data
Administrator is creating a Windows 10 VM that will be used for a virtual desktop template.
After creating the VM and booting to the ISO, the administrator is unable to install Windows
and receives the following error.
What steps does the administrator need to take to install the OS?
A. Load the Nutanix VirtIO Serial Bus Driver.
B. Load the VirtIO Network Ethernet Adaper.
C. Load the Nutanix Virtual Balloon Driver.
D. Load the Virtual SCSI pass-through controller.
Explanation: Answer: D. Load the Virtual SCSI pass-through controller.
The error message shown in the image indicates that Windows 10 setup cannot find any
drives to install the OS. This is because the Nutanix AHV hypervisor uses a virtual SCSI
pass-through controller to present disks to the VMs, and Windows 10 does not have a builtin
driver for this device. Therefore, the administrator needs to load the Nutanix VirtIO driver
for the virtual SCSI pass-through controller during the OS installation process. The Nutanix
VirtIO driver package contains various drivers that are specifically used by Windows VMs
hosted in the Nutanix environment to enhance their stability and performance1. The
administrator can download the latest Nutanix VirtIO driver package from the VirtIO
downloads page of the Nutanix support portal. The administrator can then follow these
steps to load the driver and install the OS2:
On the Windows 10 setup screen, click Load driver.
Insert a USB drive or mount an ISO image that contains the Nutanix VirtIO driver
package.
Browse to the location of the driver package and select the folder that matches the
OS architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
Select the vioscsi.inf file and click Next.
Wait for the driver to load and then click Refresh.
Select the disk where you want to install Windows 10 and click Next.
An administrator has a Custom backup application that requires a 2TB disk and runs m Windows. Throughput is considerably lower than expected.
The application was installed on a VM with the following configuration:
• FOU vCPUs with one core/vCPU
• 4GB of Memory
• One 50GB vDisk for the Windows installation
• One 2TB vDisk for the application
What is the recommended configuration change to improve throughput?
A. Add 4GB of memory to the VM
B. Increase the vCPUs assigned to the VM
C. Span the 2TB disk across four vDisks
D. Increase the number of cores per vCPU
Which data savings technique utilizes stripes and parity calculation in a Nutanix cluster?
A. Compression
B. Parity strip
C. Erasure coding
D. Deduplication
Explanation: According to the Nutanix Support & Insights web search result1, erasure coding is a data savings technique that utilizes stripes and parity calculation in a Nutanix cluster. Erasure coding increases the usable capacity on a cluster by reducing the replication factor of data blocks. Instead of replicating data, erasure coding uses parity information to rebuild data in the event of a disk or node failure. Erasure coding can save up to 50% of storage space compared to replication factor 2, and up to 75% compared to replication factor 32.
Refer to Exhibit.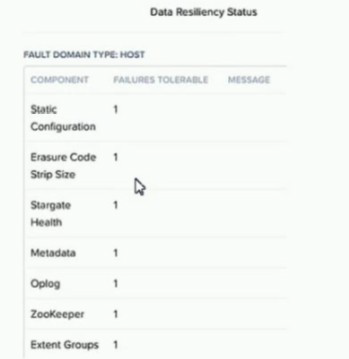
An administrator increases the cluster RF to 3. The containers are not modified.
What will the new values in the data resiliency dashboard be for FAILURES TOLERABLE
for the Zookeeper and Extent Groups components?
A. Zookeeper = 1 and Extent Groups = 1
B. Zookeeper = 2 and Extent Groups = 2
C. Zookeeper = 2 and Extent Groups = 1
D. Zookeeper = 1 and Extent Groups = 2
Explanation: According to the web search results, the cluster redundancy factor (RF)
determines how many copies of the cluster metadata and configuration data are stored on
different nodes. By default, the cluster RF is 2, which means that there are three copies of
the Zookeeper and Cassandra data on the cluster. If the cluster RF is increased to 3, then
there will be five copies of the Zookeeper and Cassandra data on the cluster12. This
means that the Zookeeper component can tolerate two failures, as it can still operate with a
quorum of three nodes out of five3.
However, the container replication factor (RF) determines how many copies of the VM data
and oplog are stored on different nodes. The container RF can be set independently for
each container, and it can be different from the cluster RF. For example, a container can have RF 2 even if the cluster has RF 34. In this case, the container will only have two
copies of the VM data and oplog on the cluster, regardless of the cluster RF. This means
that the Extent Groups component can only tolerate one failure, as it needs at least one
copy of the VM data and oplog to be available5.
Therefore, if the administrator increases the cluster RF to 3, but does not modify the
containers, then the new values in the data resiliency dashboard will be Zookeeper = 2 and
Extent Groups = 1
| Page 5 out of 30 Pages |
| Previous |