| Page 16 out of 51 Pages ... Showing Questions in Random order from Exam |
A consultant is working to setup the network before starting the Foundation process. How should the consultant complete this task?
A. Using the shared IPMI port, ensure that the connected switch can auto-negotiate to 1 Gbps.
B. Disable IPv6 on the network to which the nodes are connected to ensure that IPv6 unicast is blocked.
C. Ensure the IPMI of the nodes are reachable using pre-configured IPMI IPv6 addresses.
D. On Nutanix NX Series, connect the IPMI port and any one of the data ports to the switch.
Which container advanced setting should be configured to prevent ISO container images from exceeding a 100GB limit.
A. Reserved capacity
B. Advertised capacity
C. Erasure coding
D. Compression
The correct container advanced setting to configure in order to prevent ISO container images from exceeding a 100GB limit is "Advertised Capacity." This setting allows administrators to set a maximum storage capacity that is visible and available to the user, irrespective of the actual physical capacity available, thereby preventing over-allocation and management issues in environments where strict capacity limits are required.
During a pre-engagement call, a customer explains that network cables are missing from
the boxes. The consultant examines the bill of materials more closely to verify the quantity
and type required by the hardware. The rack is already equipped with one OOBM Ethernet
switch and two 10GbE SFP+ ToR switches.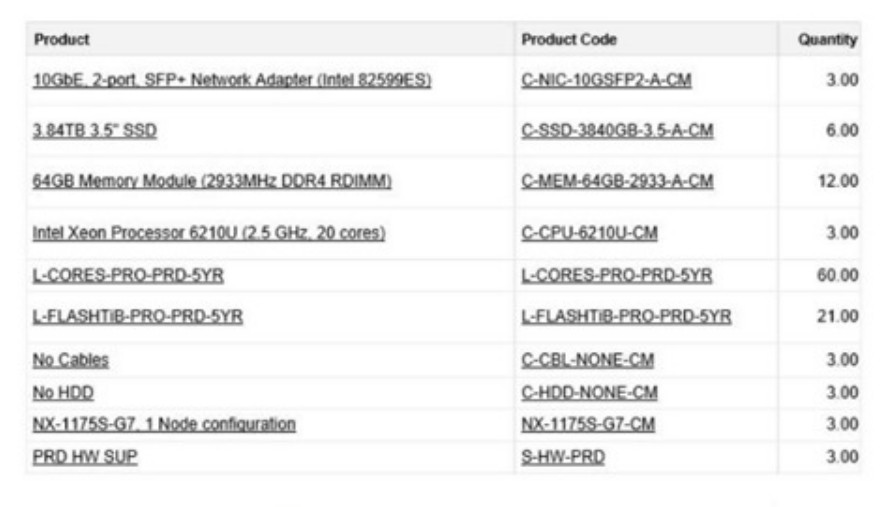
Which cables should the consultant recommend to the customer for implementing in this
scenario?
A. Six Ethernet Cat7 cables
B. Six DAC 10GbE cables and 3 Ethernet cables
C. Six lOGbE cables
D. Three DAC 10GbE cables and 3 Ethernet cables
Explanation: Considering the equipment setup with one Out-of-Band Management (OOBM) Ethernet switch and two 10GbE SFP+ Top of Rack (ToR) switches, the consultant should recommend six DAC (Direct Attach Cable) 10GbE cables and three Ethernet cables. The DAC 10GbE cables are suitable for connecting the nodes to the ToR switches to handle high-speed data transfers, while the Ethernet cables are necessary for connections related to management purposes, such as connecting to the OOBM switch for remote management tasks. This recommendation ensures adequate connectivity for both data and management networks.
During a technical call with a customer, it is identified that this installation will be software only on Dell servers. The out-of-band management interfaces will not be given IP addresses until the consultant is onsite. Which Foundation method should be used for this type of installation?
A. Bare metal using iDRAC MAC addresses.
B. Bare metal using LAN MAC addresses.
C. Bare metal using block serial numbers.
D. Bare metal using node serial numbers.
Explanation: In scenarios where a software-only installation is planned on Dell servers without pre-configured IP addresses for out-of-band management interfaces, the iDRAC MAC addresses are crucial. Using iDRAC (Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller), a consultant can perform a bare metal installation remotely and manage the servers effectively. This method is preferable when IP addresses are not initially available, allowing the consultant to utilize the out-of-band management network for setup. References: Nutanix Installation and Configuration guides, especially those pertaining to Dell hardware, available through the Nutanix Bible and official Nutanix training materials.
A consultant will be doing an install for an enterprise customer. The consultant has racked up, powered on, and connected their Foundation software to the new nodes. The Foundation VM is not discovering the hardware.
What should the consultant do to resolve this issue?
A. Console to each node, reboot the node, go through BIOS to set an IPMI IP address, then run Foundation bare metal installation using IPMI IP addresses.
B. Connect a crash cart to each node, log in to the pre-installed AHV hypervisor, run the IPMITool commands to set IPMI IP Address, subnet, and gateway for each node. Run a Foundation using the configured IPMI addresses that were just set.
C. Collect the IPMI MAC addresses on the back of each node, run a bare metal Foundation using each MAC addresses.
D. Connect a crash cart to each node, reboot the node, go through BIOS and set an IPMI IP address for each node. Using your Foundation VM, create a Phoenix boot ISO, then mount the ISO via Virtual Media connector from IPMI.
Explanation:
In a Nutanix environment, if the Foundation VM is not discovering the hardware, it could be due to issues with the IPMI (Intelligent Platform Management Interface) settings. IPMI is a set of computer interface specifications for an autonomous computer subsystem that provides management and monitoring capabilities independently of the host system’s CPU, firmware (BIOS or UEFI), and operating system.
In this scenario, the consultant should connect a crash cart to each node, log in to the pre-installed AHV hypervisor, and run the IPMITool commands to set the IPMI IP Address, subnet, and gateway for each node. After setting the IPMI settings, the consultant should run Foundation using the configured IPMI addresses that were just set.
This will ensure that the Foundation VM can communicate with the nodes via IPMI and discover the hardware, allowing the installation to proceed.
A consultant is deploying a new Nutanix cluster. The nodes have the following network
interfaces.
2x 10G NICS
2x 25G NICS
The consultant is using the default virtual switch configurations for AHV. After creating 10
VMs, the consultant observes inconsistent network speeds from the VMs on the AHV host.
What should the consultant do to resolve this issue?
A. Configure load balancing on the virtual switch for both 106 and 25G interfaces.
B. Configure a separate virtual switch with 10G NICs on vs o and 256 NICs on vs.
C. Configure Active/Backup for both the 10G and 25G interfaces.
D. Configure all network interfaces with LACP on the same virtual switch.
Explanation: To resolve inconsistent network speeds from the VMs on an AHV host equipped with both 10G and 25G NICs, the consultant should configure all network interfaces with Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) on the same virtual switch. This configuration will allow for better load balancing and bandwidth aggregation across multiple network interfaces, improving overall network throughput and reducing bottlenecks.
| Page 16 out of 51 Pages |
| Previous |